
Urban sustainability intertwines the needs of people, the planet, and prosperity, recognizing that these three elements are inherently interconnected. It urges us to rethink how we design our cities, how resources are utilized, and how we live our lives within the urban landscape. By embracing sustainable practices, urban communities are not only mitigating the environmental impact of their existence, but are also building stronger, healthier, and more resilient societies.
From eco-friendly architecture to renewable energy sources, urban sustainability encompasses a vast array of disciplines and practices. It encourages the development of clean transportation systems, the preservation of green spaces, and the promotion of sustainable consumption patterns. It inspires innovation and collaboration among politicians, architects, scientists, and citizens alike to address the myriad challenges faced by densely populated urban environments.
While the path towards urban sustainability may appear daunting, it is essential. Our cities are at the forefront of the battle against climate change, and the decisions we make today will shape the quality of life for generations to come. The benefits of embracing sustainable practices are manifold, ranging from cleaner air and water to increased social cohesion and economic prosperity.
Sustainable Transportation
Transportation plays a crucial role in urban sustainability. As cities continue to grow and evolve, the need for efficient, clean, and sustainable transportation systems becomes increasingly evident. By reimagining how we move people and goods within our urban landscapes, we can greatly contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving air quality, and enhancing the overall livability of our cities.
Public Transit
One of the cornerstones of sustainable transportation is the promotion and enhancement of public transit systems. Efficient and well-connected public transportation networks can significantly reduce the number of private vehicles on the road, thus decreasing traffic congestion and the associated carbon emissions. Investments in expanding public transit infrastructure, such as bus rapid transit (BRT) systems, light rail, and subway networks, can enhance accessibility and provide affordable and eco-friendly transportation options for urban dwellers.
Active Transportation
Active transportation refers to modes of travel that rely on human-powered means, such as walking and cycling. Encouraging and facilitating active transportation not only reduces our reliance on fossil fuels but also promotes physical activity and improves public health. By creating safe and accessible paths for pedestrians and cyclists, cities can create vibrant, interconnected communities while reducing traffic congestion and emissions.
Electric Mobility
The advent of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a significant opportunity for sustainable transportation. By replacing conventional internal combustion engine vehicles with EVs, cities can significantly reduce air pollution and carbon emissions. Supporting the development of charging infrastructure, providing incentives for EV adoption, and promoting electric public transit are critical steps towards achieving a sustainable urban transportation system.
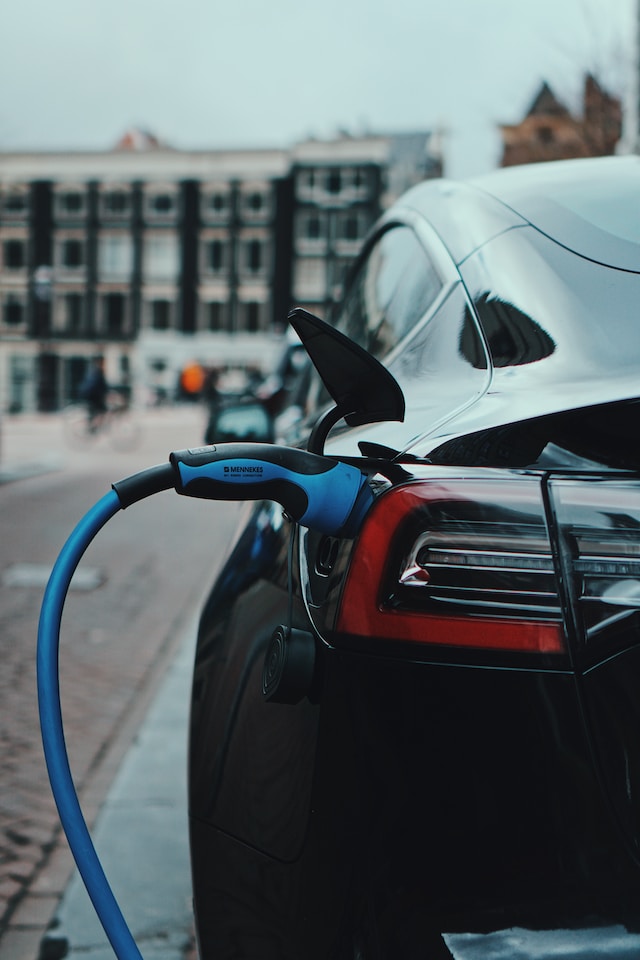
Carpooling and Shared Mobility
Promoting carpooling and shared mobility options such as ride-sharing services and bike-sharing programs can greatly reduce the number of vehicles on the road, leading to decreased traffic congestion, improved air quality, and more efficient use of urban space. Initiatives that encourage carpooling, like dedicated carpool lanes and incentives for ride-sharing, can help create a culture of shared transportation in urban areas.
Innovative Solutions
Cities must continuously explore and embrace innovative transportation solutions to address the unique challenges they face. This may include implementing smart traffic management systems to optimize traffic flow, integrating autonomous vehicles to enhance safety and efficiency, and exploring alternative modes of transportation such as electric scooters and micro-mobility options. Embracing technology and supporting research and development in sustainable transportation can play a pivotal role in shaping the future of urban mobility.
Waste Management and Recycling
Proper waste management and recycling practices are integral components of urban sustainability. As cities continue to expand and populations grow, the management of waste becomes increasingly important in minimizing environmental impact and promoting a circular economy. By reducing waste generation, implementing effective waste collection systems, and promoting recycling initiatives, urban communities can conserve resources, minimize pollution, and create a more sustainable future.
Waste Reduction
The first step in effective waste management is to reduce the amount of waste generated in the first place. Cities can encourage waste reduction through public education campaigns that promote conscious consumption, encouraging citizens to buy only what they need and reduce packaging waste.

Additionally, policymakers can collaborate with businesses to develop sustainable packaging alternatives and enforce regulations that discourage single-use plastics.
Source Separation
Source separation is a crucial practice that involves sorting waste into different categories, such as organic, recyclable, and non-recyclable materials. By implementing source separation programs, cities can maximize the recovery of valuable materials and reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. Providing residents with easily accessible recycling bins and clear instructions on proper waste sorting helps ensure successful source separation.
Effective Waste Collection Systems
Efficient waste collection systems are essential to ensure that waste is properly managed and disposed of. This includes regular garbage and recycling collection schedules, the placement of appropriate collection containers throughout the city, and ensuring that waste collection vehicles are properly maintained and equipped. By streamlining waste collection processes, cities can improve waste diversion rates and reduce the negative consequences of improper waste disposal.
Recycling Infrastructure
Investing in robust recycling infrastructure is vital for sustainable waste management. Cities can establish recycling centers and facilities capable of processing various recyclable materials, including plastics, paper, glass, and metals. Implementing technology-driven sorting systems can aid in the efficient segregation and processing of recyclables, maximizing their potential for reuse.
Composting and Organic Waste Management
Organic waste, such as food scraps and yard waste, constitutes a significant portion of urban waste. Implementing composting programs can divert organic waste from landfills, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
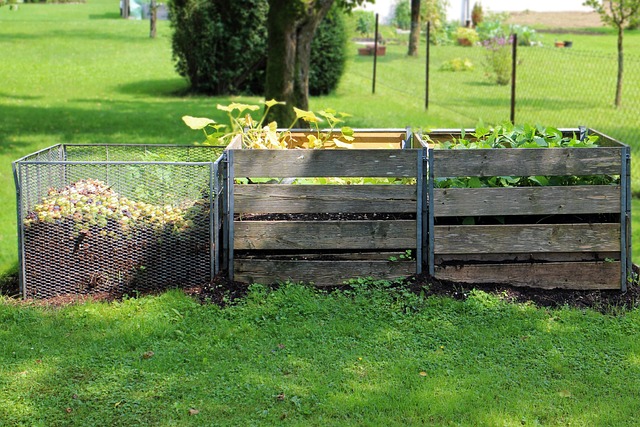

This also creates nutrient-rich soil amendments. Cities can establish community composting sites or provide composting bins for residents, promoting the circularity of resources and supporting local agriculture.
Innovative Waste Management Solutions
To further advance waste management practices, cities must embrace innovative solutions. This may include the adoption of waste-to-energy technologies, such as anaerobic digestion or incineration with energy recovery, which can convert non-recyclable waste into renewable energy sources. Exploring partnerships with private organizations, investing in research and development, and incentivizing the use of sustainable waste management technologies can drive the evolution of urban waste management.
Green Infrastructure and Urban Planning
Green infrastructure refers to the interconnected network of natural and built elements within urban areas that provide multiple benefits, including climate resilience, improved air and water quality, enhanced biodiversity, and increased quality of life for residents. Incorporating green infrastructure into urban planning is crucial for creating sustainable and livable cities that can withstand the challenges of climate change and promote human well-being.
Green Spaces and Parks
Creating and preserving green spaces, such as parks, gardens, and urban forests, is essential for urban sustainability. These green areas provide numerous benefits, including carbon sequestration, temperature regulation, stormwater management, and recreational opportunities. By integrating green spaces into urban planning, cities can combat the urban heat island effect, provide habitats for wildlife, and improve the mental and physical health of residents.
Urban Agriculture
Promoting urban agriculture is a sustainable approach to food production that can enhance food security, reduce food miles, and foster community engagement. Rooftop gardens, community gardens, and vertical farming can be integrated into urban planning to utilize underutilized spaces, improve air quality, and reconnect residents with nature. Urban agriculture also supports local economies, promotes healthy eating, and reduces the environmental impact of traditional food production systems.
Sustainable Drainage Systems
Integrating sustainable drainage systems (SuDS) into urban planning can help manage stormwater runoff, prevent flooding, and improve water quality. SuDS mimic natural processes, incorporating features such as rain gardens, permeable pavements, and retention ponds to absorb and filter stormwater runoff. By incorporating SuDS into urban landscapes, cities can reduce their reliance on costly and energy-intensive conventional drainage systems, while also providing additional green spaces.
Green Roofs and Walls
Green roofs and walls are innovative solutions that bring vegetation into the urban landscape, even in densely built environments. By covering rooftops and vertical surfaces with plants, these installations provide numerous benefits, such as reducing energy consumption, mitigating stormwater runoff, improving air quality, and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of buildings. Urban planners can incentivize the implementation of green roofs and walls through zoning regulations and financial incentives.

Energy Efficiency and Smart Cities
Energy efficiency and smart city initiatives are essential in promoting sustainable urban development. By incorporating innovative technologies and sustainable practices, cities can reduce energy consumption, decrease greenhouse gas emissions, and enhance the quality of life for residents. Energy efficiency encompasses a wide range of strategies, from energy-efficient buildings to smart grid systems, all of which contribute to a more sustainable and resilient urban environment.
Energy-efficient Buildings
Implementing and enforcing stringent building codes and standards can ensure that new constructions meet specific energy efficiency requirements. This includes guidelines for insulation, energy-efficient lighting, HVAC systems, and renewable energy integration.
Retrofitting existing buildings with energy-efficient technologies can significantly reduce energy consumption. Upgrading insulation, installing energy-efficient appliances, and implementing smart building management systems can optimize energy use and reduce utility costs.
Encouraging developers to pursue green building certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), helps support sustainable construction practices and ensures that buildings meet rigorous sustainability criteria.
Smart Grid Systems
Deploying Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) enables real-time energy monitoring and demand management. It allows consumers to track their energy usage and make informed decisions to reduce consumption during peak demand periods.
Implementing demand response programs encourages consumers to reduce energy use during times of high demand. With smart grid technology, consumers can receive real-time pricing information and make energy-conscious choices.
Promoting the integration of DERs, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems, into smart grid systems enhances energy resilience, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and enables localized energy generation.
Energy-efficient Street Lighting:
Replacing traditional street lights with LED fixtures significantly reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs. LED lighting is more durable, has a longer lifespan, and emits less heat, providing energy-efficient and environment-friendly illumination options for cities.
Integrating smart lighting systems with motion sensors and dimming capabilities can further optimize energy use. These systems adjust lighting levels based on pedestrian activity, reducing energy waste during low-demand periods.
Rethinking how we design our urban landscapes, utilize resources, and live our lives can create vibrant, resilient, and inclusive communities. Sustainable transportation, effective waste management, green infrastructure, and energy efficiency are all crucial components of this transformative journey. As we navigate the challenges posed by climate change and rapid urbanization, it is vital that we collaborate, innovate, and embrace the opportunities that urban sustainability presents.


